Requirements Engineering (RE) is a crucial phase in software and system development that focuses on identifying, analyzing, documenting, and managing the needs and constraints of stakeholders.
It involves understanding what the system should do, how it should behave, and under what conditions it must operate. In simple terms, Requirements Engineering ensures that developers build the right product that truly satisfies user expectations and business goals.

- Whether a team is working on a physical product or building a digital solution, requirements are essential at every stage of development. They provide clear direction by defining what needs to be built and how the final product is expected to function. Without well-defined requirements, product development becomes uncertain and unreliable.
- Projects that start without requirements often rely on assumptions rather than facts. Such guesswork increases the risk of errors, delays, and failure. Clear requirements act as a roadmap, helping teams make informed decisions and stay aligned with project objectives.
- However, simply writing down requirements is not enough to ensure success. For requirements to be truly effective, they must be carefully analyzed, prioritized according to business value, properly documented, and validated with stakeholders. In addition, they need to be continuously monitored and managed as the project evolves.
- This is where Requirements Engineering (RE) plays a vital role. Requirements Engineering is a structured process that helps teams identify, refine, and manage requirements so they remain clear, realistic, and aligned with overall project goals. By applying RE practices, organizations can significantly reduce risks and improve project outcomes.
- The impact of effective requirements management is clearly reflected in project success rates. Industry research shows that a large percentage of project failures are directly linked to poor handling of requirements, highlighting the critical role Requirements Engineering plays in delivering successful projects.
What is Requirements Engineering?Breaking It Down
Requirements Engineering is the systematic process of gathering, clarifying, validating, and maintaining requirements throughout the lifecycle of a software or system project.
It includes activities such as requirement elicitation (collecting information from users and stakeholders), requirement specification (writing clear and precise requirements), requirement validation (checking that requirements are correct and complete),Requirements Analysis (Refining & Prioritizing Requirements) and requirement management (handling changes and priorities over time).
The main objective is to create a solid foundation for design and development by minimizing misunderstandings and ambiguities.
Requirements Engineering is a fundamental part of the product development process. It provides a systematic way to gather, examine, and organize requirements so that a product can be developed with clarity and purpose.
Through Requirements Engineering, stakeholder needs are carefully analyzed and translated into clear, understandable, and actionable requirements. These requirements act as a bridge between business expectations and technical implementation, ensuring that development teams know exactly what needs to be built and why.
Moreover, the use of appropriate Requirements Engineering tools helps teams manage this process more efficiently. Such tools support documentation, tracking, and validation of requirements throughout the development lifecycle. As a result, teams can reduce misunderstandings, minimize rework, and deliver dependable products that consistently align with stakeholder expectations.
Importance in Software / System Development
Requirements Engineering plays a vital role in the success of any software or system project. Poorly defined or incomplete requirements are one of the leading causes of project failure, cost overruns, and schedule delays.
By clearly defining what the system should do, RE helps reduce rework, avoid unnecessary features, and improve communication between developers, users, and other stakeholders. It also supports better planning, testing, and quality assurance, because tests can be designed directly from well‑documented requirements.
In complex systems, such as safety‑critical or large‑scale software, proper Requirements Engineering is essential to ensure reliability, security, and compliance with regulations.
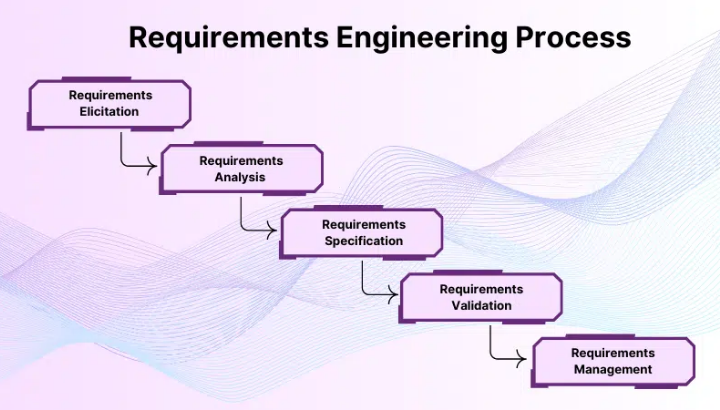
The Requirements Engineering Process: 5 Key Steps for Success
The success of any product development project largely depends on how well its requirements are defined and managed. Clear requirements provide direction, reduce uncertainty, and help teams stay aligned with project objectives. Without a structured approach, requirements can become unclear, incomplete, or inconsistent, leading to costly rework and project delays.
The Requirements Engineering process offers a systematic framework to handle requirements effectively throughout the project lifecycle. It involves a series of well-defined steps that help teams identify stakeholder needs, analyze their feasibility, document them clearly, and manage changes efficiently. By following these key steps, organizations can improve communication, reduce risks, and increase the chances of delivering a successful product.
- requirement elicitation
- requirement specification
- requirement validation
- requirement management
- Requirements Analysis (Refining & Prioritizing Requirements)
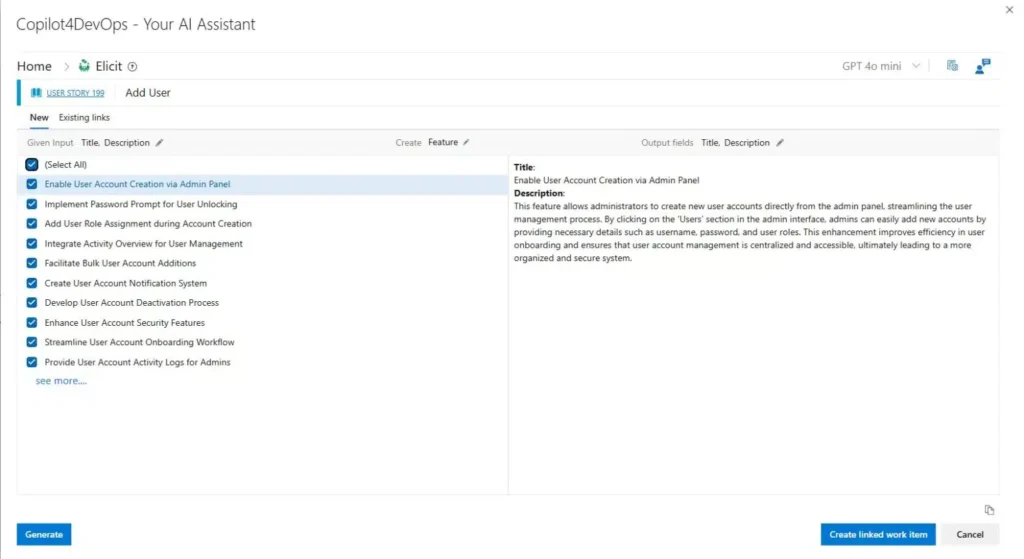
Step 1: Requirements Elicitation (Gathering Needs & Expectations)
The Requirements Engineering process begins with requirements elicitation, which focuses on identifying and collecting requirements from all relevant sources. At this stage, requirements engineers work closely with stakeholders to understand what the product should achieve and what expectations must be fulfilled.
This step plays a crucial role in eliminating ambiguity at an early stage. By clearly capturing stakeholder needs before development starts, teams can reduce misunderstandings, prevent scope creep, and ensure that everyone shares a common understanding of the project goals.
To perform effective requirements elicitation, teams can apply several proven techniques:
- Stakeholder Communication: Regular interaction with stakeholders such as product owners, developers, and project managers helps uncover both explicit and hidden requirements.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Gathering feedback through surveys allows teams to collect requirements from a broader group of users in a structured manner.
- Rapid Prototyping: Creating simple prototypes enables stakeholders to visualize the product early and provide valuable feedback that helps refine requirements.
- Document Analysis: Reviewing existing product documents, reports, or specifications helps teams gain deeper insights into the product and identify missing or unclear requirements.
In addition, modern tools and AI-powered solutions can further enhance this step. For example, AI-assisted requirements management tools integrated with development platforms can automatically extract requirements from unstructured text and convert them into actionable work items. This not only saves time but also improves accuracy and consistency throughout the requirements engineering process.
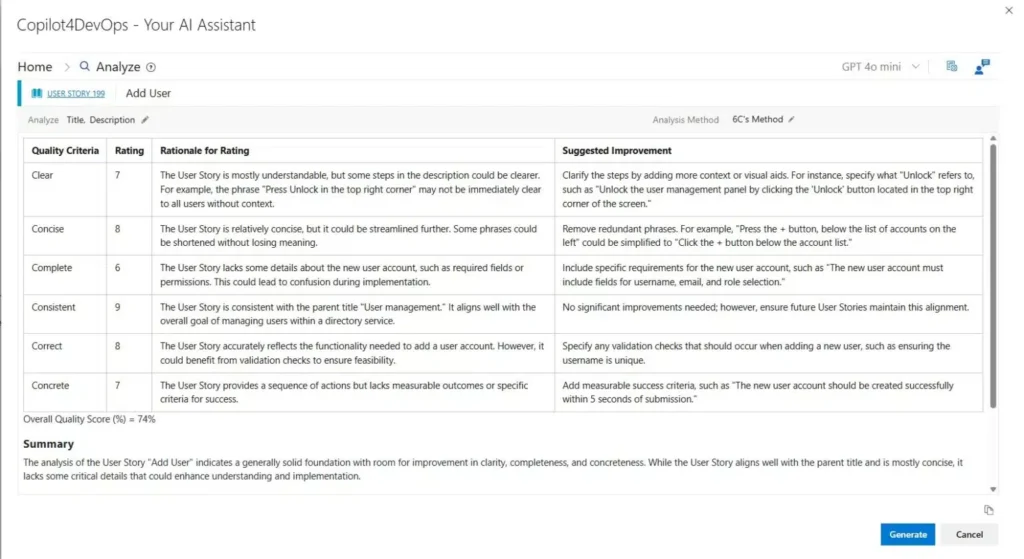
Step 2: Requirements Analysis (Refining & Prioritizing Requirements)
Simply listing requirements is not enough to begin product development. If requirements are unclear, conflicting, or poorly defined, they can create confusion and lead to costly mistakes later in the project. This is why requirements analysis is a critical step in the Requirements Engineering process.
During this phase, teams carefully examine the collected requirements to ensure they are complete, consistent, and feasible. The goal is to refine raw requirements into well-defined and actionable statements that can be confidently used during development.
Key activities involved in requirements analysis include:
- Requirement Categorization: Requirements are classified into functional and non-functional categories. Functional requirements describe what the system is expected to do, while non-functional requirements focus on performance, reliability, security, and other quality attributes.
- Requirement Prioritization: Since resources are limited, not all requirements can be implemented at once. Teams must identify which requirements are critical, which add value, and which can be deferred. Prioritizing high-impact requirements helps optimize time, cost, and effort.
- Requirement Filtering: Duplicate, conflicting, or unrealistic requirements are identified and removed. This step improves clarity and prevents inconsistencies that could disrupt development.
Advanced requirements engineering tools can further support this phase by applying structured analysis frameworks and prioritization techniques. Such tools help assess the quality of requirements, highlight gaps, and recommend improvements, enabling teams to make more informed and objective decisions.
Step 3: Requirements Specification (Documenting Clearly & Accurately)
At this stage of the Requirements Engineering process, requirements have already been identified and analyzed. However, without proper documentation, even well-defined requirements can lead to misunderstandings later in the project. Relying on assumptions to resolve such issues is risky and often results in errors.
This is why clear and accurate documentation is essential. Well-documented requirements serve as a single source of truth that teams can refer to whenever questions or conflicts arise. Instead of depending on memory or informal discussions, teams can resolve uncertainties by consulting documented requirements.
Effective requirements documentation usually begins with an overview of the product. This includes the product’s purpose, objectives, key definitions, and a glossary to ensure a shared understanding among all stakeholders. Following this, detailed functional, non-functional, and system requirements are documented along with relevant descriptions, acceptance criteria, and test cases.
In practice, requirements are commonly written in structured formats such as user stories or use cases. For example, a user story might state: “As a user, I want to sign up using my Google account so that I can access the platform quickly.” Such formats help teams clearly understand user needs and expected system behavior.
Modern requirements management tools can further enhance this step by providing structured documentation features. Tools integrated with development platforms offer reusable templates and smart documentation modules that help maintain consistency, improve readability, and ensure that requirements remain aligned throughout the project lifecycle.

Step 4: Requirements Validation (Ensuring Accuracy & Feasibility)
Once requirements are documented, it is essential to validate them to ensure they are accurate, feasible, and aligned with stakeholder needs. Validation helps prevent misunderstandings, reduces rework, and ensures that the project is built on a solid foundation.
Key Activities in Requirements Validation:
- Review Requirements Documents: Carefully examine each requirement to ensure it is clear, complete, and testable.
- Check Alignment with Stakeholder Needs: Confirm that all requirements reflect the goals and expectations of stakeholders.
- Feasibility Assessment: Ensure that each requirement can realistically be implemented within project constraints (time, budget, and technology).
- Collect Stakeholder Feedback: Use structured reviews to gather input from stakeholders and clarify any doubts.
- Incorporate Feedback: Update and refine requirements based on feedback to improve accuracy and clarity.
- Use Validation Tools: Modern tools like requirements management platforms offer review modules to send documents for stakeholder feedback, track changes, and maintain transparency.
By thoroughly validating requirements, teams can confidently move forward, knowing that the requirements are accurate, actionable, and achievable. This step ensures a smoother development process and reduces the risk of errors or misalignment later in the project.
Step 5: Requirements Management (Tracking & Updating Requirements Over Time)
Requirements are not static ,they can evolve as projects progress or as stakeholder needs change. Effective requirements management ensures that all changes are tracked, reviewed, and implemented in a controlled manner without disrupting the project workflow.
Proper management helps maintain clarity, reduces errors, and ensures that the development team always works with the most up-to-date requirements. It also provides a clear history of changes for future reference.
Key Activities in Requirements Management:
- Track Changes: Monitor any updates or modifications to requirements to ensure nothing is overlooked.
- Version Control: Maintain versions of requirements documents to keep a clear record of what has changed and when.
- Traceability: Establish links between requirements and related work items, test cases, or deliverables to understand their impact.
- Review and Approval: Ensure all changes are reviewed by relevant stakeholders before implementation.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly check for inconsistencies, conflicts, or outdated requirements throughout the project lifecycle.
- Use Management Tools: Modern tools provide features such as version history, traceability matrices, notifications, and dashboards to streamline requirements management.
By actively managing requirements, teams can adapt to changes smoothly, maintain alignment with stakeholder expectations, and increase the chances of delivering a successful product on time and within budget.
Why Does Effective Requirements Engineering Matter? The Big Benefits
Following a structured and effective Requirements Engineering (RE) process is crucial for the success of any product development project. When teams properly implement RE practices, it helps minimize risks, improves efficiency, and ensures that the final product meets the intended requirements.
The main benefits of effective Requirements Engineering:
- Reduces Misunderstandings: Clear and validated requirements help prevent confusion between stakeholders and development teams. By defining expectations upfront, the risk of misinterpretation is significantly reduced.
- Improves Communication: Well-documented requirements act as a common reference for all team members. This improves collaboration between developers, project managers, and other stakeholders.
Example: NASA’s Mars Climate Orbiter mission failed because different teams used different measurement units. A proper RE process with standardized documentation could have prevented the $327 million loss. - Cost-Effective Development: By specifying requirements early in the project, teams can accurately estimate budgets, allocate resources effectively, and avoid unnecessary expenses during development.
- Increases Development Efficiency: Requirements Engineering provides a clear roadmap for the development process. Teams know exactly what needs to be built and how, which accelerates progress and reduces wasted effort.
- Supports Compliance and Regulatory Standards: Documenting requirements related to legal or industry regulations ensures the product meets compliance standards, helping avoid penalties or legal issues.
Effective Requirements Engineering not only reduces project risks but also creates a foundation for delivering high-quality products on time and within budget.
Common Requirements Engineering Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them!)
Requirements Engineering can be challenging, and mistakes in this process often lead to delays, increased costs, or even project failure. Here are some common mistakes teams make and practical ways to avoid them:
- Incomplete Requirements:
Not all requirements are always properly documented, which can result in confusion and issues during development.
Solution: Maintain comprehensive requirements documents and update them regularly to capture all necessary details. - Lack of Stakeholder Involvement:
If stakeholders are not actively engaged in requirements elicitation and validation, the requirements may not reflect business needs accurately.
Solution: Conduct regular meetings and feedback sessions with stakeholders to ensure alignment. - Ignoring Non-Functional Requirements:
Many teams focus only on functional requirements, overlooking aspects like performance, security, usability, and reliability. Ignoring these can cause serious problems later.
Solution: Include non-functional requirements in documentation and consider them during validation and testing. - Poor Traceability:
Without proper traceability tools, it becomes difficult to track requirements and understand how they relate to other work items or deliverables.
Solution: Use tools like traceability matrices to map requirements to design, development, and testing activities. Modern requirements management platforms provide this functionality easily. - Constantly Changing Requirements:
Frequently changing requirements can result in rework, missed deadlines, and budget overruns.
Solution: Perform impact analysis before implementing changes to understand the effects on other requirements, timelines, and resources.
By being aware of these common pitfalls and applying proactive measures, teams can improve the efficiency of their requirements engineering process and significantly increase the chances of project success.
Agile vs. Traditional: How Does Requirements Engineering Change?
Requirements Engineering (RE) is influenced greatly by the development methodology used. Different approaches traditional versus agile affect how requirements are collected, analyzed, and managed throughout the project.
Traditional Methodologies (e.g., Waterfall):
- Follow a linear, sequential approach to software development.
- RE is primarily performed at the beginning of the project.
- Requirements are gathered, analyzed, documented, and approved before development starts.
- Changes later in the process are often costly, time-consuming, and difficult to implement.
- Suitable for projects with well-defined, stable requirements.
Agile Methodologies:
- Use an iterative and incremental approach, breaking the product into smaller, manageable portions called sprints or iterations.
- Requirements Engineering occurs continuously throughout the project.
- RE adapts to evolving stakeholder needs and feedback during each iteration.
- Changes are easier to accommodate, reducing the risk of costly rework.
- Encourages close collaboration between development teams and stakeholders for real-time validation of requirements.
Key Difference:
| Aspect | Traditional | Agile |
|---|---|---|
| Timing of RE | Mostly upfront | Iterative & continuous |
| Flexibility | Low; changes costly | High; adaptive to change |
| Stakeholder Involvement | Limited after initial phase | Continuous feedback & collaboration |
| Risk of Rework | Higher if requirements change | Lower due to iterative validation |
Closing Thoughts: Mastering Requirements for a Better Product
Requirements Engineering plays a crucial role in product development across industries—whether it’s healthcare, finance, aerospace, or IT. Without clearly defined requirements, teams face the risk of misalignment, costly rework, and failed project outcomes. By following the structured 5-step Requirements Engineering process, teams can ensure that requirements are well-documented, actionable, and aligned with project goals.
One important piece of advice is to leverage the right tools to streamline the requirements engineering process. Modern platforms like Requirements4DevOps (MR4DevOps) offer comprehensive solutions for teams working within Azure DevOps environments.
MR4DevOps transforms the way requirements are captured, connected, and managed throughout the project lifecycle. Key features include:
- Smart Documentation & Baselining: Create structured, reusable documents that maintain consistency across projects.
- Visual Modeling: Represent requirements visually to improve understanding and communication.
- Impact Analysis: Evaluate the effect of requirement changes before implementing them.
- End-to-End Traceability: Track requirements from inception through development and testing without leaving the DevOps environment.
By utilizing modern requirements management tools, teams can reduce errors, prevent rework, improve efficiency, and stay consistently aligned with stakeholder expectations. Mastering requirements engineering not only enhances product quality but also ensures projects are delivered on time and within budget

